Statistical studies conducted during the year 2017 estimated approximately 20 million people with RA or Rheumatoid Arthritis. It is a chronic condition that can affect the major joints in the body. Various types of rheumatoid arthritis can affect elbows, wrists, knees, pelvis, phalangeal joints and cause extreme pain which is also accompanied by inflammation, redness and strained mobility. In severe cases, the condition may also lead to partial or complete immobility thereby requiring surgical procedures.
Rheumatoid Arthritis commonly affects individuals from late teens to senior citizens but is quite rare among young children. The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can be reduced by continuous physical therapy and pain killers in order to decrease the inflammation and help to cope up with the pain.
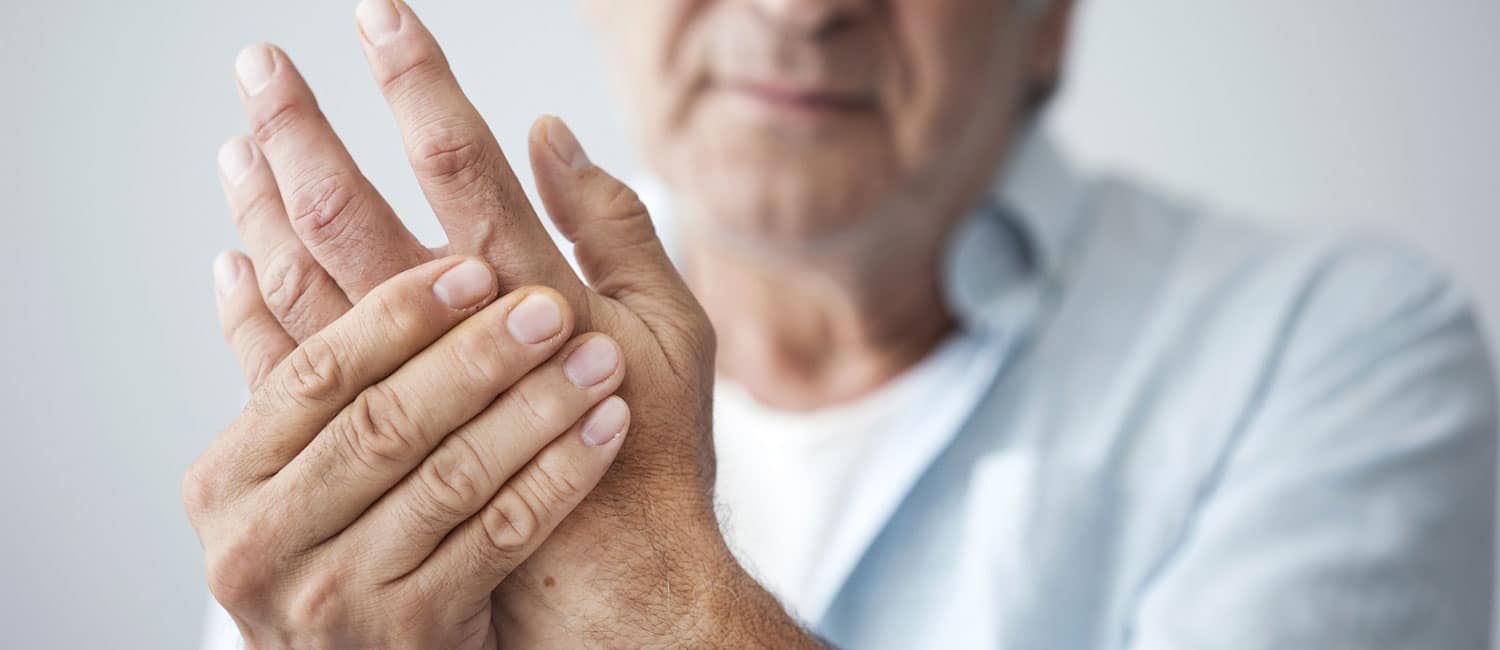
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis is chronic in nature and is an autoimmune disorder, in which the defense system of the body fails to distinguish between own and foreign cells and thus, end up destroying its own cells. Such a situation may arise due to a number of metabolic changes.
Though the condition is not directly related to the genetic anomaly and is not hereditary, the presence of certain types of genes may increase the chances of the condition. Individuals with high risk are screened for the presence of such genetic markers and are thus provided with necessary medical attention. Where several genes have been isolated after intense research, mutational changes in Human Leukocyte Antigen abbreviated as the HLA gene poses a greater threat to the individual possessing it. Among them, the HLA-DRB1 is significantly marked and screened for, primarily.
Types of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the body’s defense mechanism starts to attack its own cells and tissues thereby causing inflammation, pain, and swelling. However, such an anomaly is generally triggered by two types of chemicals, which are:
- Tumor Necrosis Factor, abbreviated as TNF
- Interleukin 1
Based on this, Rheumatoid Arthritis can be distinguished and thus carefully treated. Apart from this, Rheumatoid Arthritis can be further divided into two distinct categories based on the presence of specific RF protein, which are:
- Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis: The presence of Rheumatoid Factor protein in suspected candidates confirms the occurrence of Rheumatoid Arthritis and thus assists in early recognition of the condition. In addition to this, the presence of anti-CCPs as well as ACPAs, (specific antibodies towards which the Rheumatoid Factors are directed) may also be detected.
- Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis: In this condition, the candidate lacks the RF protein. However, the candidate tested is diagnosed with mild RA and shall require further confirmatory tests for the same.
Treatments Available
A number of treatments are available for curing Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medications are mostly restricted Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic drugs which are also known as DMARDs. DMARDs help in reducing the symptoms to a great extent by easing the autoimmune response of the body. DMARDs are not specific for RA but can be implemented for various other autoimmune diseases in the body. Apart from that, the other medications prescribed for RA are NSAIDs or Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, painkillers, for relieving inflammation as well as pain. The other available treatments include:
- Heat therapy: Application of heat pads on inflamed areas can help to cope up with pain
- Physical therapy
- Arthrocentesis: Draining of fluid from the affected or swollen regions via needles.
- Surgical procedures: Two types of surgical procedures are commonly performed in individuals affected with Rheumatoid Arthritis, which are:
- Arthroplasty: Surgical curing or a damaged joint to relieve the symptoms and increase the mobility of the individual.
- Joint Replacement procedure: Partial or complete replacement of the affected joint by a prosthesis.
Success Rates
The most successful treatment options are providing DMARDs, whereas, in extreme cases, surgical procedures provide the ultimate result. These two procedures flaunt high success rates and are helpful in relieving the symptoms to a great extent. Prolonged treatments in the initial stage along with other available treatments often help the individual in retaining a normal and healthy life. The important factors in achieving high success records are adapting to preventing measures for restricting disease progression, which can be achieved by immunotherapy treatments. However, a major drawback of the treatment is that it weakens the body’s defense mechanism and thus, makes it prone to several other diseases. Thus, the candidates are advised to have regular follow-ups and report even for minor cough and cold.

